
🔬 Have you ever wondered why your skin suddenly looks dull, wrinkled, or aged beyond its years? The culprit might be hiding in plain sight – free radicals. These microscopic troublemakers are constantly bombarding your skin, wreaking havoc on its health and appearance.
But what exactly are free radicals, and why should you care? Imagine tiny molecular saboteurs, roaming freely in your body, causing chaos wherever they go. These unstable atoms are on a mission to steal electrons from healthy cells, leaving a trail of damage in their wake. Your skin, being the largest organ and your first line of defense, bears the brunt of this invisible assault. The result? Premature aging, dark spots, and a complexion that's lost its luster.
Don't despair just yet! Understanding the science behind free radicals and their impact on your skin is the first step towards reclaiming your youthful glow. In this blog post, we'll dive deep into the world of free radicals, exploring their origins, the visible effects they have on your skin, and most importantly, how you can fight back. From environmental factors that increase your exposure to the power of antioxidants, we'll equip you with the knowledge and tools to keep your skin radiant and resilient. Let's embark on this journey to unlock the secrets of skin health and turn back the clock on free radical damage! 💪🏼✨
What Are Free Radicals?
A. Definition and basic concept
Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause damage to our cells, including skin cells. These molecules are missing an electron, making them highly reactive and eager to steal electrons from other molecules. This process, known as oxidation, can lead to a chain reaction of cellular damage.
B. Types of free radicals
There are several types of free radicals that can affect our skin:
-
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
-
Reactive Nitrogen Species (RNS)
-
Hydroxyl radicals
-
Superoxide anions
| Free Radical Type | Primary Source | Potential Damage |
|---|---|---|
| ROS | Oxygen metabolism | DNA damage, lipid peroxidation |
| RNS | Nitric oxide reactions | Protein modification, cell death |
| Hydroxyl radicals | Water molecule breakdown | Severe DNA and protein damage |
| Superoxide anions | Cellular respiration | Enzyme inactivation, inflammation |
C. How free radicals form in the body
Free radicals form in our bodies through various processes:
-
Normal cellular metabolism
-
Exposure to environmental toxins
-
Immune system responses
-
Stress and inflammation
D. Natural sources of free radicals
While our bodies produce some free radicals naturally, external factors can significantly increase their formation:
-
UV radiation from sunlight
-
Air pollution
-
Cigarette smoke
-
Alcohol consumption
-
Processed foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats
Understanding these sources is crucial for developing strategies to protect our skin from free radical damage. Now that we've explored what free radicals are and where they come from, let's delve into the science behind how they specifically affect our skin.
The Science Behind Free Radicals and Skin Damage
Oxidative stress explained
Oxidative stress occurs when there's an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in your body. This imbalance can lead to cellular damage, particularly in your skin. Here's a breakdown of the process:
-
Free radicals accumulate
-
Antioxidant defenses are overwhelmed
-
Cellular structures are damaged
-
Skin health is compromised
| Factor | Normal State | Oxidative Stress State |
|---|---|---|
| Free Radicals | Balanced | Excessive |
| Antioxidants | Sufficient | Depleted |
| Cellular Health | Maintained | Compromised |
How free radicals attack skin cells
Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that steal electrons from nearby stable molecules, causing a chain reaction of damage. In skin cells, this attack can occur in several ways:
-
Lipid peroxidation of cell membranes
-
DNA damage
-
Protein oxidation
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction
Impact on collagen and elastin
Collagen and elastin, the proteins responsible for skin's firmness and elasticity, are prime targets for free radical damage. The oxidative stress:
-
Breaks down existing collagen fibers
-
Inhibits new collagen production
-
Alters elastin structure
-
Reduces skin's ability to "bounce back"
Accelerated aging process
The cumulative effect of free radical damage leads to premature aging of the skin. This manifests as:
-
Fine lines and wrinkles
-
Loss of skin elasticity
-
Uneven skin tone
-
Age spots and hyperpigmentation
Understanding this science is crucial for developing effective strategies to protect and rejuvenate your skin. Next, we'll explore the visible effects of free radicals on skin, which will help you identify potential damage and take action.
Visible Effects of Free Radicals on Skin
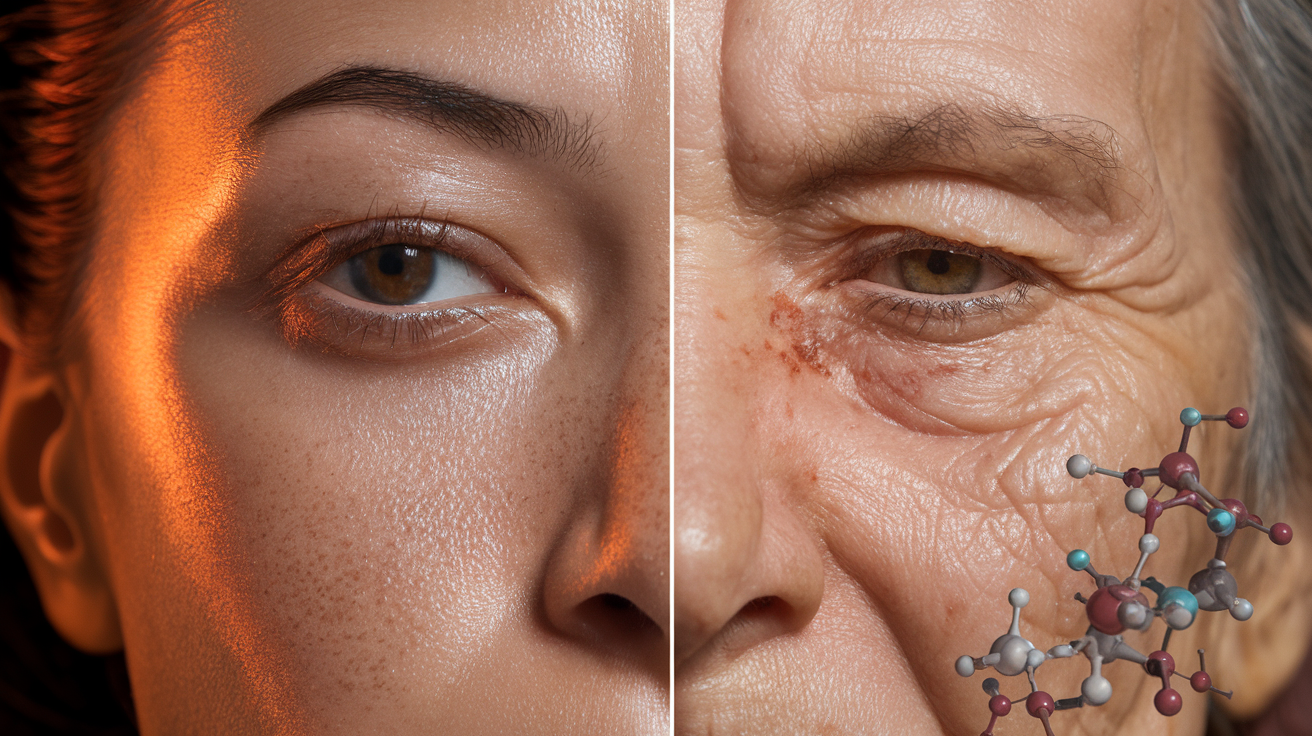
Premature wrinkles and fine lines
Free radical damage accelerates the breakdown of collagen and elastin, leading to the formation of premature wrinkles and fine lines. These visible signs of aging typically appear first around the eyes, mouth, and forehead.
Uneven skin tone and hyperpigmentation
Oxidative stress caused by free radicals can trigger an overproduction of melanin, resulting in:
-
Dark spots
-
Age spots
-
Uneven skin tone
-
Melasma
Loss of skin elasticity
Free radicals attack the skin's structural proteins, causing:
-
Sagging skin
-
Loss of firmness
-
Decreased bounce and resilience
Increased sensitivity and inflammation
The damage inflicted by free radicals can compromise the skin barrier, leading to:
-
Redness and irritation
-
Increased susceptibility to environmental stressors
-
Heightened sensitivity to skincare products
| Free Radical Effect | Visible Sign | Common Areas Affected |
|---|---|---|
| Collagen breakdown | Wrinkles | Eyes, mouth, forehead |
| Melanin overproduction | Hyperpigmentation | Cheeks, forehead |
| Protein degradation | Sagging | Jawline, neck |
| Barrier compromise | Sensitivity | Entire face |
These visible effects of free radical damage underscore the importance of protecting your skin from oxidative stress. By understanding these signs, you can take proactive steps to shield your skin from further harm and potentially reverse some of the existing damage.
Environmental Factors That Increase Free Radical Exposure

UV radiation and sun damage
UV radiation is one of the primary sources of free radical damage to our skin. When our skin is exposed to sunlight, it triggers a cascade of chemical reactions that generate harmful free radicals. These unstable molecules can cause oxidative stress, leading to premature aging and skin damage.
| UV Type | Wavelength | Effects on Skin |
|---|---|---|
| UVA | 315-400 nm | Penetrates deep, causes premature aging |
| UVB | 280-315 nm | Causes sunburn, damages DNA |
| UVC | 100-280 nm | Blocked by ozone layer, highly dangerous |
To protect your skin from UV-induced free radical damage:
-
Use broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30+) daily
-
Wear protective clothing and seek shade
-
Avoid peak sun hours (10 am - 4 pm)
Air pollution and toxins
Urban environments expose our skin to various pollutants that can increase free radical production. These include:
-
Particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10)
-
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
-
Nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide
These pollutants can penetrate the skin barrier, leading to oxidative stress and inflammation. To combat this, consider:
-
Using antioxidant-rich skincare products
-
Cleansing thoroughly at the end of each day
-
Incorporating air-purifying plants in your living space
Smoking and alcohol consumption
Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption significantly contribute to free radical formation in the body. Cigarette smoke contains thousands of chemicals that generate free radicals, while alcohol metabolism produces reactive oxygen species.
Poor diet and lifestyle choices
A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can increase free radical production. Conversely, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants can help neutralize these harmful molecules. Consider incorporating:
-
Colorful fruits and vegetables
-
Whole grains and lean proteins
-
Green tea and other antioxidant-rich beverages
Additionally, stress and lack of sleep can exacerbate free radical damage. Prioritize stress management techniques and aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support your body's natural defenses against free radicals.
Antioxidants: Your Skin's Natural Defense

What are antioxidants?
Antioxidants are molecules that protect your skin cells from damage caused by free radicals. They act as your skin's natural defense system, neutralizing harmful molecules before they can wreak havoc on your cells. These powerful compounds can be found in various sources, including:
-
Fruits and vegetables
-
Skincare products
-
Supplements
How antioxidants neutralize free radicals
The neutralization process involves a simple yet effective mechanism:
-
Donation of electrons
-
Stabilization of free radicals
-
Prevention of chain reactions
| Antioxidant Action | Effect on Free Radicals |
|---|---|
| Electron donation | Stabilizes free radicals |
| Chain-breaking | Halts oxidative damage |
| Metal chelation | Prevents metal-catalyzed oxidation |
Key antioxidants for skin health
Several antioxidants play crucial roles in maintaining skin health:
-
Vitamin C: Boosts collagen production and brightens skin
-
Vitamin E: Moisturizes and protects against UV damage
-
Retinol (Vitamin A): Promotes cell turnover and reduces fine lines
-
Niacinamide: Improves skin barrier function and reduces inflammation
-
Green tea extract: Combats inflammation and photoaging
Incorporating antioxidants into your skincare routine
To maximize the benefits of antioxidants, consider these tips:
-
Layer products with different antioxidants for synergistic effects
-
Apply antioxidant serums in the morning for daytime protection
-
Use antioxidant-rich moisturizers at night for overnight repair
-
Consume a diet rich in colorful fruits and vegetables
By understanding and harnessing the power of antioxidants, you can significantly improve your skin's defense against free radical damage. Next, we'll explore lifestyle changes that can further combat free radical damage and promote overall skin health.
Lifestyle Changes to Combat Free Radical Damage

Sun protection strategies
Protecting your skin from the sun is crucial in combating free radical damage. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher
-
Wear protective clothing, including wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses
-
Seek shade during peak sun hours (10 am to 4 pm)
-
Reapply sunscreen every 2 hours or after swimming/sweating
| Sun Protection Method | Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Sunscreen | High |
| Protective Clothing | Very High |
| Seeking Shade | Moderate |
| Time of Day Avoidance | High |
Nutrition for skin health
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants can help neutralize free radicals. Focus on:
-
Colorful fruits and vegetables (berries, leafy greens, citrus fruits)
-
Omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts)
-
Green tea and other antioxidant-rich beverages
-
Foods high in vitamins C and E (bell peppers, almonds, avocados)
Exercise and its impact on free radicals
Regular exercise can boost your body's natural antioxidant defenses. However, balance is key:
-
Aim for 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week
-
Include both cardio and strength training in your routine
-
Stay hydrated during workouts to support skin health
-
Consider outdoor exercises in the early morning or late evening to minimize sun exposure
Stress management techniques
Chronic stress can increase free radical production. Implement these stress-reduction strategies:
-
Practice mindfulness meditation
-
Try deep breathing exercises
-
Engage in yoga or tai chi
-
Pursue hobbies and activities you enjoy
Importance of quality sleep
Quality sleep is essential for skin repair and free radical neutralization. Prioritize sleep by:
-
Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule
-
Creating a relaxing bedtime routine
-
Ensuring your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool
-
Limiting screen time before bed to improve sleep quality
By incorporating these lifestyle changes, you can significantly reduce free radical damage and promote healthier, more resilient skin.

Free radicals pose a significant threat to our skin's health and appearance, accelerating the aging process and causing visible damage. Understanding these unstable molecules and their impact on our skin is crucial for developing an effective skincare routine. By recognizing the environmental factors that increase free radical exposure and implementing lifestyle changes, we can take proactive steps to protect our skin.
Incorporating antioxidant-rich products into your skincare regimen and making conscious lifestyle choices can significantly reduce free radical damage. Remember, healthy skin starts from within, so focus on a balanced diet, stay hydrated, and protect your skin from excessive sun exposure. By taking these steps, you'll be well on your way to maintaining youthful, radiant skin and combating the harmful effects of free radicals.
📚 References
- Lobo V et al., 2010 – Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health
- Pandel R et al., 2013 – Oxidative stress in skin aging
- Masaki H, 2010 – Role of antioxidants in the skin: anti-aging and photoprotection
- Draelos ZD, 2003 – Topical antioxidants in dermatology: benefits and limitations
- Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2018 – Plant polyphenols and flavonoids as natural antioxidants in skincare
- Rinnerthaler M et al., 2015 – Oxidative stress and aging: mechanisms and skin impact
- Poon F et al., 2015 – Mechanisms of oxidative damage and the role of antioxidants in dermatology




Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.